Management¶
The chapter explains how to manage CloudCIX after installation.
Validate new Servers added to Region¶
Turn off Robot, via the Portal, open the Admin App menu “Setup > Roles > Robot”. Select the Address (region) the server was added to. From the list of users, select “Remove Robot” for the active user.
Build a new VM using the specs of the server added e.g. SSD, HDD, Hyper-V (Windows VM), KVM (Linux VM)
In the database you will need to update the server id of the VM above to the id of the new server
UPDATE vm SET server_id = <new_server_id> WHERE id = <vm_id>
<new_server_id>: ID of the Server added to region
<vm_id>: ID of the VM built in step 2
Turn on Robot, via the Portal, open the Admin App menu “Setup > Roles > Robot”. Select the Address (region) the server was added to. From the list of users, select “Add Robot” for the user deactivated in step 1.
During these steps, 403 (permission) errors will be reported to Kibana as the API credentials for Robot are no longer for a user that has the role robot. This is expected and will stop being reported once the role has been reasigned in step 4.
Unresourced Infrastructure¶
If Virtual Infrastructure is placed in an Unresourced state by Robot this indicates that Robot was unable to complete a routine task on the hardware and manual intervention is required to investigate and resolve. An email will be sent to the support team with the details of the object, what action the customer requested and the message returned from the hardware.
e.g.
An error occurred while processing VR #999.
Task: update
Exception:
[‘Unable to load configuration changes onto Router ::1 ]
A more detailed response will be reported to Kibana to aid the Support Team. Once the Support Team has resolved the issue with the hardware, the database needs to be manually updated to either:
Place the virtaul infrastructure’s state back into the state requested by the customer to allow Robot to complete the customer’s request
or
The action taken by the Support Team as completed the customer’s request so the virtual infrastructure needs to be placed in a stable state.
Task |
Customer Requested State |
Stable State |
|---|---|---|
create |
Requested (1) |
Running (4) |
update (from a running state) |
Running Update (10) |
Running (4) |
update (from a quiesced state) |
Quiesced Update (15) |
Quiesced (5) |
quiesce |
Quiesce (5) |
Quiesced (6) |
restart |
Restart (7) |
Running (4) |
scrub |
Scrub (8) |
Closed (18) |
UPDATE <virtual_infrastructre> SET state = <state> WHERE id = <id>
If back to customer requested state need to set run_robot for virtual infrastructure’ project
UPDATE project SET run_robot = True WHERE id = <project_id>
<virtual_infrastructure>: The item to update e.g. virtaul_router, vm
<state>: The state object needs to be placed in based on the above table
<id>: The ID of the object. This can be obtained from the email e.g. 999 is the ID of the virtual router in the sample email above
<project_id>: This can also be obtained from the email as it will also include the response from the API robot retrieved to execute.
Robot Offline¶
A robot is considered offline if it’s heartbeat reported on Grafana is flat lining.
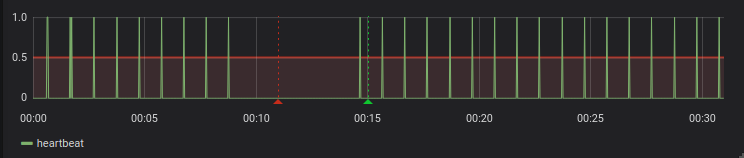
A robot being offline does not affect the current existing virtual infrastructure built in a region. What it does mean is that any new requests to build or update virtual infrastructure will not be executed until the robot is back online.
To retrieve the logs and restart a robot ssh onto the robot host and run the following commands:
Log into robot docker container: Run
sudo docker exec -it robot bash
Move to the /tmp directory: Run
cd /tmp/
List files in /tmp directory: Run
ls
Copy the contents of every file with stderr in the name by running “cat filename” and paste into a txt file. Send file onto developers@cloudcix.com
Stop robot and robot-worker: Run
sudo docker stop robot robot-worker
Start robot and robot-worker: Run
sudo docker start robot robot-worker